FLEXIBLE PACKAGING: BAGS AND SACKS
Flexible packages are the ones made from elastic—flexible materials which are easily formed after filling them with a product. The main material used in production is plastics (Figure 1). To the flexible packages belong films and flexible laminates used as wrapping of the product and the package. They are used in retail and institutional food and non-food as well as in industrial applications, retail, consumer storage and trash bags, bags, wraps, shrink, and stretch films. (Figure 2)
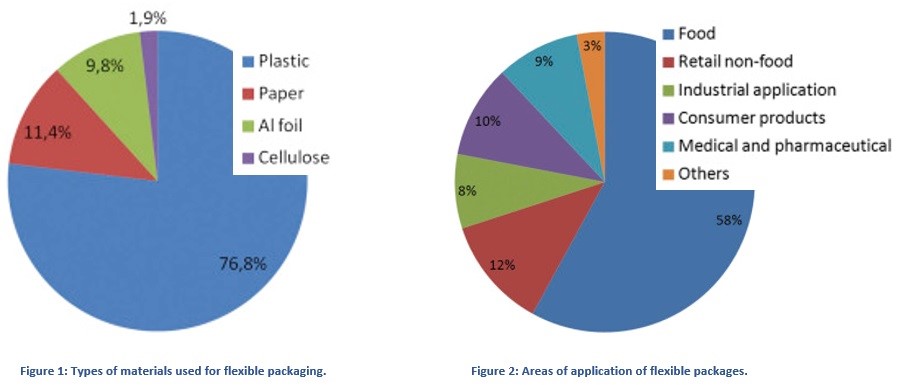
The most numerous group of flexible packaging are bags and sacks-in 2014, they constituted 34% of the worldwide market of flexible packages. When producing bags, sacks, and pouches, two or more edges of the film or laminate are welded together in order to contain the product. The bags may also be welded from film or from a tubing. The laminates, in turn, are used to produce stand-up pouch, retort pouch, pillow pouch, pouches with spouts, and so on

Stand-up pouches, also called Doypacks, are welded bags with a well-formed bottom which allow it to stand. They are made from various laminates printed on the interlayer basis and their multicolor prints are very significant for marketing. Such packages are applied to pack not only drinks and juice, but also sauces, mayo, oils, or liquid soaps, as well as dry products such as coffee, tea, spices, dried fruit, nuts, and sweets.
Retort pouches are the type of pouches made from laminates, plastic films, and aluminum foils. They may be formed by welding from four sides (pillow pouch) or as a stand-up pouch with a bottom. Such packages are an alternative for metal cans and allow for packaging food and drinks in sterile processes. They are commonly used to pack ready-to-eat meals which may be eaten cold or may be heated in a package.
COMMONLY USED RESINS AND SUBSTRATES IN FLEXIBLE PACKAGING BAGS AND SACKS
1. RESIN AND SUBSTRATE FUNCTION
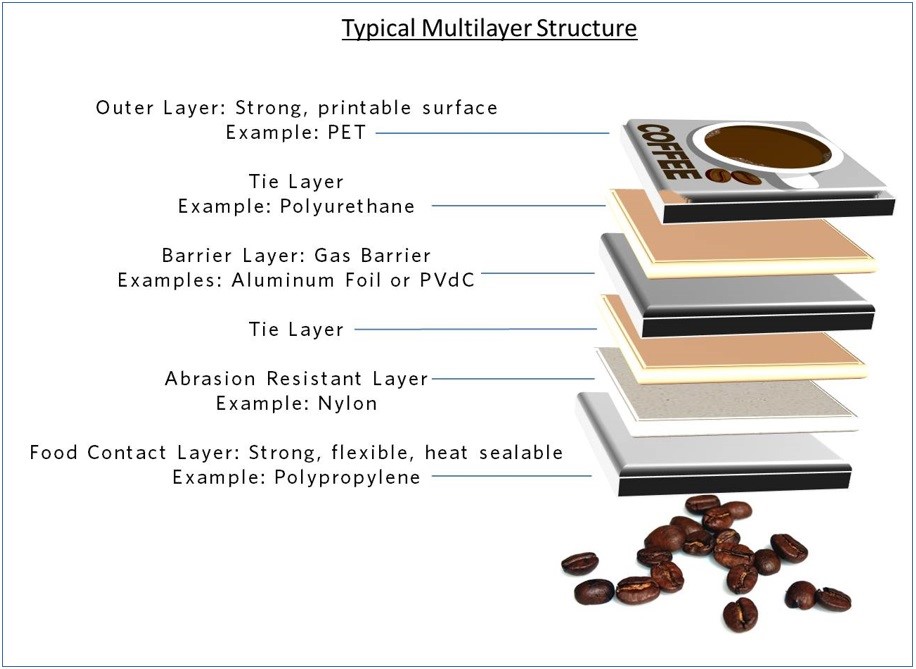
the basic purpose of a flexible package is to provide protection (including structural integrity, barrier, sealing, and adhesion) and promotion (which may include aesthetics, printability, and so on). In multilayer films, a specific combination of materials is selected to meet the functional requirements in the most economical manner. Often materials used in flexible packaging provide more than one function. For example, high density polyethylene (HDPE) in a cereal liner bag-in-box structure provides stiffness, puncture resistance, and moisture barrier. As more layers are incorporated into flexible packaging, the contribution of the each of the layers has become more specialized.
1.1 STRUCTURAL INTEGRITY
Stiff materials are generally used for structural integrity, such as paper, oriented polypropylene (OPP), or oriented polyester (OPET).
1.2 BARRIER
Moisture, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and light barrier are the four most common barrier needs in flexible packaging. Oil and grease barrier is another need for some applications. The amount of barrier required depends on the product being packaged and the shelf life requirements. HDPE and polypropylene (PP) are often the most cost-effective moisture barrier materials. Aluminum foil and metallized film are also used for moisture barrier. Polar polymers such as ethylene vinyl alcohol (EVOH), polyvinyl alcohol (PVOH), and PVDC provide an outstanding oxygen barrier performance. Aluminum foil and metallized film also provide an exceptional oxygen barrier.
1.3 SEALING
The sealant layer is the innermost layer of the flexible packaging structure. Its chief function is to provide a hermetic seal to keep the contents of the package in and contamination out. Therefore, polymers with low melting points generally make good sealants. As a class, the ethylene copolymers such as ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) copolymer, low density polyethylene (LDPE), linear low density polyethylene (LLDPE), and ionomers have low melting points and provide low seal initiation temperature.
Tyypillinen pakkauksen monikerrosrakenne
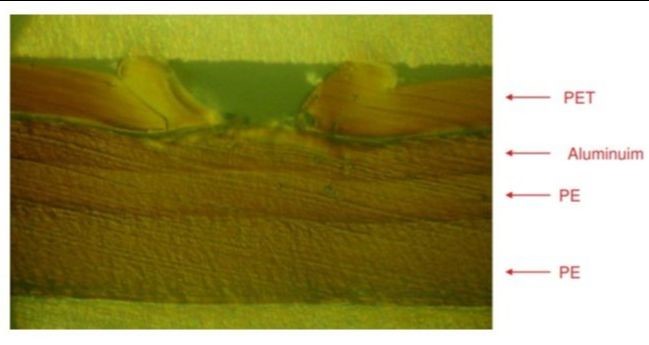
TYPICAL MATERIAL COMBINATIONS IN LAMINATED BAGS AND SACKS PACKAGING.
WITH ALUMINIUM
WITHOUT ALUMINIUM

EASY OPEN ON BAGS AND SACKS BY LASER SCORING
The packaging industry has seen a rise in demand for features that add convenience and value to a package while maintaining the integrity of the product inside.
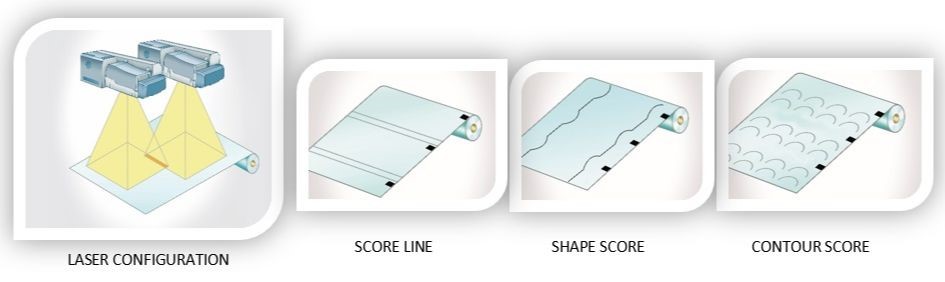
Laser-converting systems produce an accurate score with needed high speeds
The packaging industry has seen a rise in demand for features that add convenience and value to a package while maintaining the integrity of the product inside. With this increase, it becomes clear that packaging suppliers must adapt to the evolving needs of consumers by seeking out process solutions that deliver convenience and quality. Laser-scoring systems for flexible films deliver versatile value-added packaging features that enhance a product’s ease of use without compromising the structural integrity of a flexible film.
Laser scoring of flexible films is a non-contact, clean processing solution that eliminates the need for mechanical tooling or consumables. A fully digital workflow markedly reduces production downtime, as pattern or design modifications can be made instantaneously. Laser modules can easily be integrated into new material handling systems or can be retrofitted to existing systems on a production floor. These laser systems are capable of precise scoring processes that add accurate features not obtainable through mechanical methods.
THE DIGITAL ADVANTAGE
Applications for laser scoring are diverse and include easy-open tear strips for resealable standup pouches, pour spouts, microwavable packages, and peel-away windows. Advancements in laser-scoring technology no longer limit options simply to straight line, down-web processing, and thereby expand package design opportunities. For example, contour score lines can be added to slider zipper pouches. When opened, the top material is discarded, leaving the sliding zipper exposed and allowing the consumer to more easily operate the slider and access the product inside.
While mechanical methods exist for scoring flexible materials, these options often yield an unreliable score line that unevenly tears and degrades a package without providing consumers an easy-open solution. Laser-converting systems produce a more accurate, functional score while matching the high speeds of today’s manufacturing environments. An entirely digital workflow eliminates expensive machine downtime; production changeover is achieved simply by opening a new file. Laser-scoring systems deliver user-friendly and value-added features that protect the quality of the product inside.
SEI LASER – PACKMASTER: A UNIQUE SOLUTION FOR EASY OPENING ON BAGS AND SACKS PACKAGING

THE IMPORTANCE OF EASY-TO-OPEN PACKAGING
Surveys have revealed the consumer’s annoyance and frustration with packages that are difficoult to open – vexation that customers rank above concerns about whether tha package is “smart”, “innovative”, or even “sustainable”.
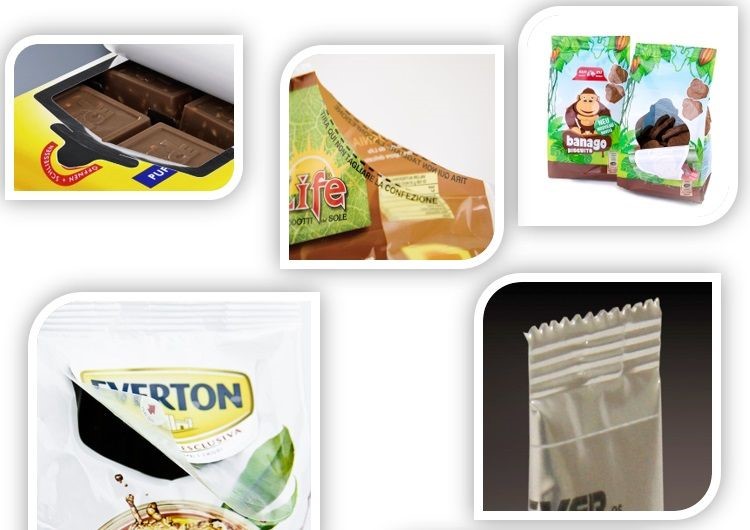
Easy opening technologies by laser system for flexible packaging can be used to create an integral opening of any size, shape or position on a pack.
We can find numerous benefits of this solution:
1. Replacing the tear tape strips, zips, or closures
2. Can be used in numerous laminated structures
3. Creative design with added value of an easy open
4. Enable re-closable solutions

Read more about flexible packaging

